
A histogram may also be normalized to display "relative" frequencies showing the proportion of cases that fall into each of several categories, with the sum of the heights equaling 1.
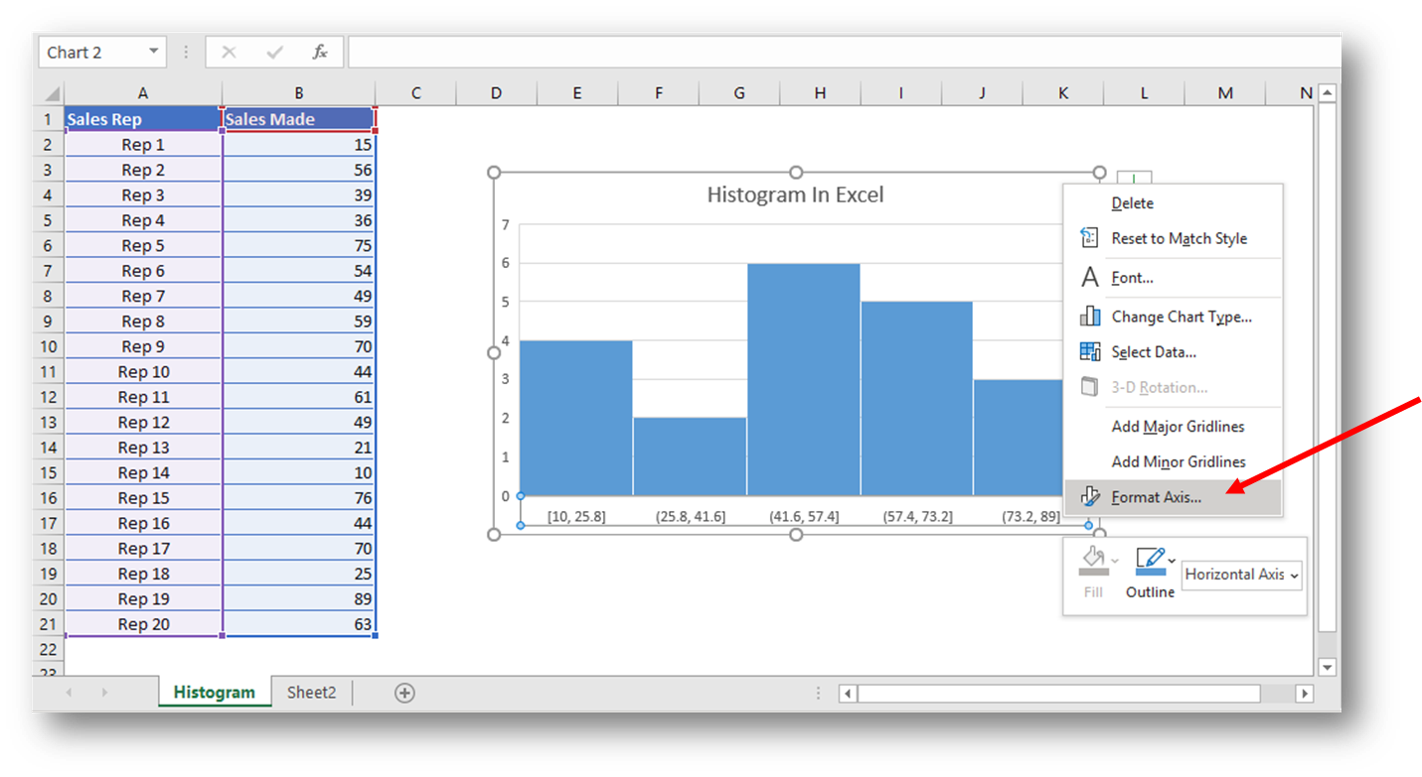
If the bins are of equal size, a bar is drawn over the bin with height proportional to the frequency-the number of cases in each bin. The bins (intervals) must be adjacent and are often (but not required to be) of equal size. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping intervals of a variable. To construct a histogram, the first step is to " bin" (or " bucket") the range of values-that is, divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals-and then count how many values fall into each interval. The term was first introduced by Karl Pearson. To roughly assess the probability distribution of a given variable by depicting the frequencies of observations occurring in certain ranges of values.Ī histogram is an approximate representation of the distribution of numerical data. For the histogram used in digital image processing, see Image histogram and Color histogram.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
